Total Hip Replacement
Hip replacement surgery is the final option for painful hip joint with reduced mobility leading to difficulty in activities of daily living . In this surgery the surgeon removes the damaged sections of the hip joint and replaces them with parts usually constructed of metal, ceramic and very hard plastic. This artificial joint (prosthesis) helps reduce pain and improve function. Also called total hip arthroplasty, hip replacement surgery might be an option if hip pain interferes with daily activities and nonsurgical treatments haven’t helped or are no longer effective. Arthritis damage is the most common reason to need hip replacement.
Anatomy
The hip is one of the body’s largest joints. It is a ball-and-socket joint. The socket is formed by the acetabulum, which is part of the pelvis bone. The ball is the femoral head, which is the upper end of the femur (thighbone). The bone surfaces of the ball and socket are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth tissue that cushions the ends of the bones and enables them to move easily.
A thin tissue called the synovial membrane surrounds the hip joint. In a healthy hip, this membrane makes a small amount of fluid that lubricates the cartilage and eliminates almost all friction during hip movement. Bands of tissue called ligaments (the hip capsule) connect the ball to the socket and provide stability to the joint.
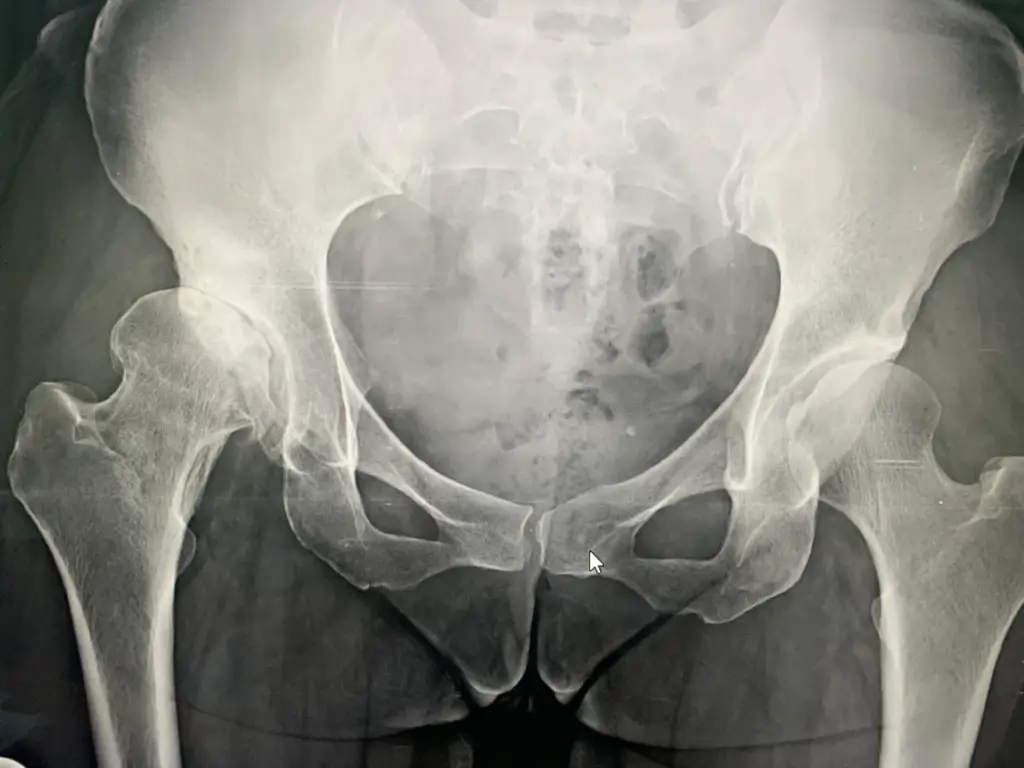
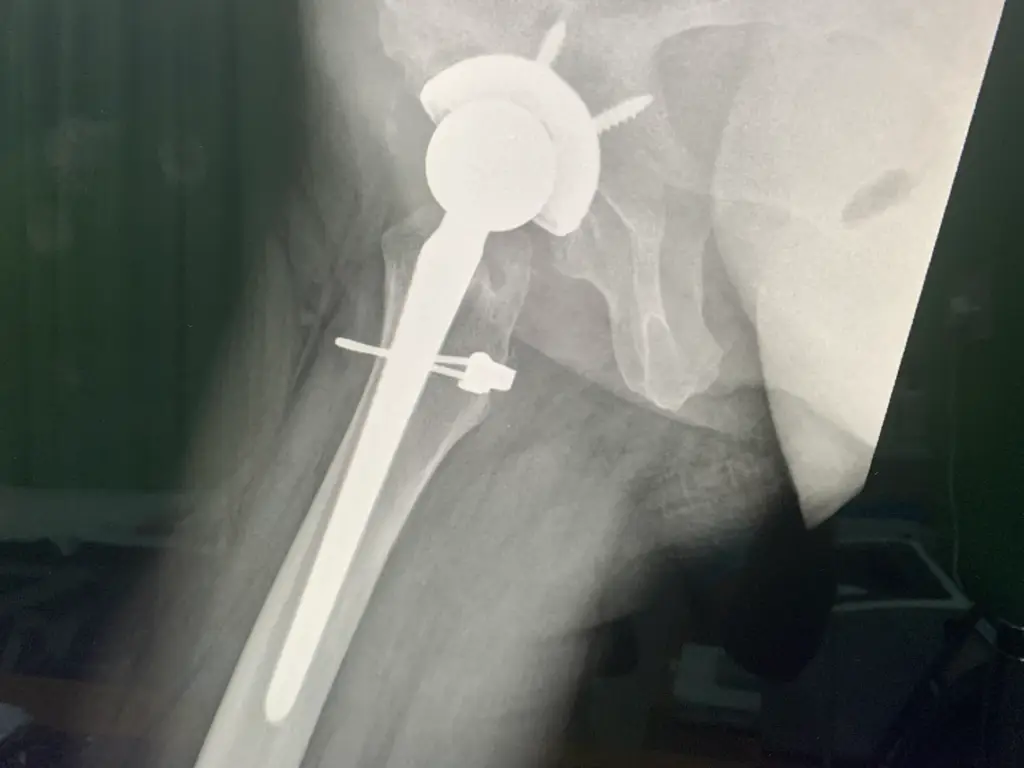
Why it’s done?
Conditions that can damage the hip joint, sometimes making hip replacement surgery necessary, include:
- Osteoarthritis:
Commonly known as wear-and-tear arthritis, osteoarthritis damages the slick cartilage that covers the ends of bones and helps joints move smoothly.
- Rheumatoid arthritis:
Caused by an overactive immune system, rheumatoid arthritis produces a type of inflammation that can erode cartilage and occasionally underlying bone, resulting in damaged and deformed joints.
- Osteonecrosis:
If there isn’t enough blood supplied to the ball portion of the hip joint, such as might result from a dislocation or fracture, the bone might collapse and deformity occurs .
When Surgery Is Recommended?
- Persists, despite pain medication
- Worsens with walking, even with a cane or walker
- Interferes with sleep
- Affects the ability to walk up or down stairs
- Makes it difficult to rise from a seated position

